The Fonic alphabet was invented by Andrea Vaccari in 1991. It is a phonoanalogic and phonosymbolic alphabet, which like the IPA is designed for the phonetic transcription of all the languages of the world, but it can be also used for the normal writing of national languages, in simplified variants, which provide language specific features, called implosions, for representing a phones sequence by a single symbol, which however preserves the phonoanalogic representation of each phone.
The term phonoanalogic is intended to describe those symbols that visually reproduce the characteristics of the phonatory production of the phones they represent, while phonosymbolic refers to those symbols that conventionally describe them (Vaccari 2018)[1].
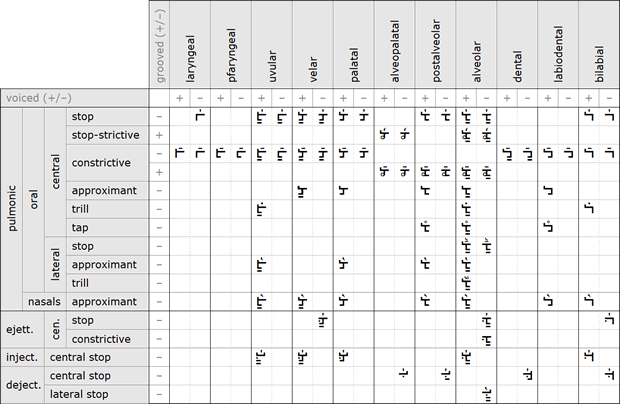
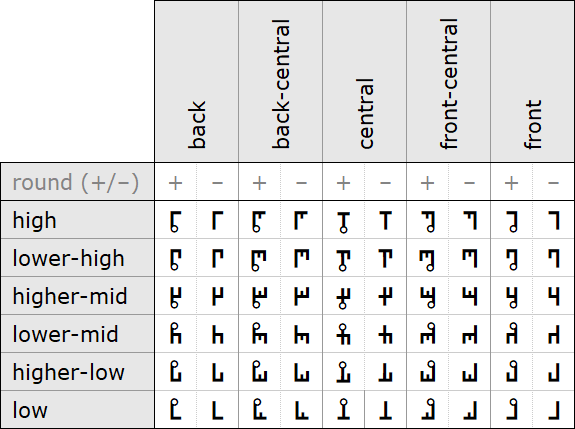
Consonants are displayed below in a slightly different structure from that of the IPA, as for example the nasal feature is not considered a manner of articulation, but a separate parameter, concerning the outlet of the air flow, so that wie have a main division between oral and nasal consonants. Oral consonants are then divided into central and lateral, as the lateral feature is also not considered a manner of articulation. Furthermore, stops with nasal release are considered nasal stops, and stops with lateral release are considered lateral stops. The terms stop-strictive and constrictive of the articulatory phonetic are here used instead of the terms africate and fricative of the auditory phonetic (Canepari 2007)[2].

Ĉiuj homoj estas denaske liberaj kaj egalaj laŭ digno kaj rajtoj. Ili posedas racion kaj konsciencon, kaj devus konduti unu la alian en spirito de frateco.
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They
are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
(Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights)
Information about Fonic
http://fonic.altervista.org/basic/web/en-US/wiki/fonic.html
http://fonic.altervista.org/basic/web/en-US/wiki/fonic-italian.html
http://fonic.altervista.org/basic/web/en-US/wiki/phonoanalogic.html
http://fonic.altervista.org/basic/web/en-US/wiki/phonosymbolic.html
Constructed scripts for: Ainu | Arabic | Chinese languages | Dutch | English | Hawaiian | Hungarian | Japanese | Korean | Lingala | Malay & Indonesian | Persian | Tagalog / Filipino | Russian | Sanskrit | Spanish | Taino | Turkish | Vietnamese | Welsh | Other natural languages | Colour-based scripts | Tactile scripts | Phonetic/universal scripts | Constructed scripts for constructed languages | Adaptations of existing alphabets | Fictional alphabets | Magical alphabets | A-Z index | How to submit a constructed script
[top]
You can support this site by Buying Me A Coffee, and if you like what you see on this page, you can use the buttons below to share it with people you know.

If you like this site and find it useful, you can support it by making a donation via PayPal or Patreon, or by contributing in other ways. Omniglot is how I make my living.
Note: all links on this site to Amazon.com, Amazon.co.uk
and Amazon.fr
are affiliate links. This means I earn a commission if you click on any of them and buy something. So by clicking on these links you can help to support this site.
[top]