English belongs to the Anglo-Frisian branch of the Germanic language family. It is related to Scots, Dutch, Frisian and other Germanic languages. It has a significant amount of vocabulary from Old Norse, Norman French, Latin and Greek, and loanwords from many other languages.
There are about 1.2 billion speakers of English. Some 350 million people speak English as a native language, and a further 850 million speak it as a second or foreign language. Countries where English is widely spoken include: the UK, Ireland, the USA, Australia, New Zealand, Canada, Singapore, Malaysia, Malta, Cyprus, Barbados, Marshall Islands, Jamaica, Bermuda, British Virgin Islands, US Virgin Islands, Dominica, Palau, Grenada, Guyana, Trinidad and Tobago, Bahamas, Suriname, Vanuatu, Anitgua and Barbuda, Saint Kitts and Nevis, the Cayman Islands, Nigeria, Ghana, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Belize, the Philippines, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Israel, Austria, Germany, Finland, Switzerland and Belgium [source].
English evolved from the Germanic languages brought to Britain by the Angles, Saxons, Jutes and other Germanic tribes from about the 5th Century AD. These languages are known collectively as Anglo-Saxon or Old English, and began to appear in writing during the 5th century AD in a runic alphabet.
English acquired vocabulary from Old Norse after Norsemen starting settling in parts of Britain, particularly in the north and east, from the 9th century. To this day varieties of English spoken in northern England contain more words of Norse origin than other varieties of English. They are also said to retain some aspects of pronunciation from Old Norse.
The Norman invasion of 1066 brought with it a deluge of Norman and Latin vocabulary, and for the next three centuries English became a mainly oral language spoken by ordinary people, while the nobility spoke Norman, which became Anglo-Norman, and the clergy spoke Latin. When English literature began to reappear in the 13th century the language had lost the inflectional system of Old English, and the spelling had changed under Norman influence. For example, the Old English letters þ (thorn) and ð (eth) were replaced by th or y, is in Ye Olde Shope. This form of English is known as Middle English.
By about the 15th century Middle English had evolved into Early Modern English, and continued to absorb numerous words from other languages, especially from Latin and Greek. Printing was introduced to Britain by William Caxton in around 1469, and as a result written English became increasingly standardised. The first English dictionary, Robert Cawdrey's Table Alphabeticall, was published in 1604.
During the medieval and early modern periods English spread from England to Wales, Scotland and other parts of the British Isles, and also to Ireland. From the 17th century English was exported to other parts of the world via trade and colonization, and it developed into new varieties wherever it went. English-based pidgins and creoles also developed in many places, such as on islands in the Caribbean and Pacific, and in parts of Africa.

A recording of the English alphabet by Simon Ager (British English)
A recording of the English alphabet by Kathleen Loden (American English)
This chart shows the vowels and diphthongs used in standard varieties of English spoken in the USA, Australia, England, Canada, Ireland, New Zealand, South Africa, Scotland and Wales. There is significant variation in the vowel sounds used within most of these countries, and in other countries where English is spoken.
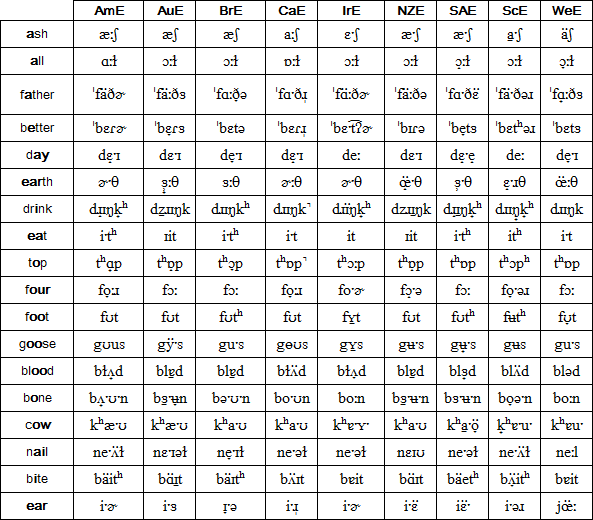
Source: http://www.soundcomparisons.com
AmE = American English (General American), AuE = Australian English, BrE = British English (RP), CaE = Canadian English, IrE = Irish English, NZE = New Zealand English, SAE = South African English, ScE = Scottish English, WeE = Welsh English
A recording of the English vowels by Simon Ager (British English)
A recording of English vowels by Kathleen Loden (American English)
A recording of the English consonants by Kieran Booth (Australian English)
| Letters | IPA | Examples | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| b | [b] | bee/sob | |
| c/k/ck/q | [kʰ/k] | car/skill/quack | [kʰ] initially, [k] elsewhere |
| ch/t | [tʃʰ/tʃ] | chain/nature | [tʃʰ] initially, [tʃ] elsewhere |
| d | [d] | dog | |
| f/ff/gh/ph | [f] | faff/tough/photo | |
| g | [g] | grand | |
| h | [h] | hand | initial h not pronounced in some dialects |
| j/g/dg | [dʒ] | judge/gin | |
| l | [l] | laugh | |
| m | [m] | moon | |
| n | [n] | note | |
| ng/n | [ŋ] | sing/linger/drink | |
| p | [pʰ/p] | pig/spot/top | [pʰ] initially, [p] elsewhere |
| r | [ɹʷ/ɹ/ɾ] | read | varies between dialects |
| s/ss/c | [s] | sock/lass/city | |
| sh/s/ti | [ʃ] | share/sure/emotion | |
| t | [tʰ/t] | tea/stick/let | [tʰ] initially, [t] elsewhere |
| th | [θ] | three/fifth | |
| th | [ð] | the/mother | |
| v/f | [v] | voice/of | |
| w/u | [w] | wet/quiet | |
| x | [ks/ɛks] | box/x-ray | |
| y | [j] | yacht | |
| z | [z/s] | zoo/prose | |
| s/ge/z | [ʒ] | measure/beige/seizure | |
| ch | [x] | loch | appears in Scottish English |
A recording of the English vowels by Simon Ager (British English)
A recording of English consonants by Kathleen Loden (American English)
A recording of the English consonants by Kieran Booth (Australian English)
See an interactive chart of (American English) phonemes
https://www.langademy.com/learn-languages/english/improve-pronunciation/
Download an alphabet chart for English (Excel speadsheet)
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
(Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights)
[ɔːl ˈhjuːmən ˈbiːɪŋz ə bɔːn friː ənd ˈiːkwəl ɪn ˈdɪgnɪtɪ ənd raɪts ðeɪ ə ɪnˈdaʊd wɪð ˈriːzn ənd ˈkɒnʃəns ənd ʃʊd ækt təˈwɔːdz wʌn əˈnʌðə ɪn ə ˈspɪrɪt ɒv ˈbrʌðəhʊd]
[ɔːl ˈhjuːmən ˈbiːɪŋz ɑːr bɔːrn friː ænd ˈiːkwəl ɪn ˈdɪgnɪtiː ænd raɪts ðeɪ ɑːr enˈdaʊd wɪð ˈriːzən ænd ˈkɑːnʃəns ænd ʃʊd ækt təˈwɔːrdz wʌn əˈnʌðər ɪn ə ˈspɪrɪt əv brʌðərˌhʊd]
A recording of this text in British English by Simon Ager (Received Pronunication)
A recording of this text by Kathleen Loden (American English)
Recordings of this text by people from different English-speaking countries and regions.
If you speak another variety of English or with a different accent, it would be great to have a recording of this text. Please send it to feedback[at]omniglot[dot]com.
Information about English | Phrases | Numbers | Time | Family words | Tongue twisters | Tower of Babel | Articles | Books | Links
Information about the English Language
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/English_language
https://www.britannica.com/topic/English-language
http://oxforddictionaries.com/page/thehistoryofenglish/the-history-of-english
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/History_of_the_English_language
Online English language courses
http://www.bbc.co.uk/worldservice/learningenglish/
http://www.english-language-school.info
http://www.eslcafe.com/search/Online_English_Courses/
http://www.speaklanguages.com/english/
http://www.polite-english.com
http://www.english-daily.com
http://www.english-portal.com
http://www.urdu-english.com/lessons.php
http://www.theenglishalley.es
http://www.englishokay.com
http://learnenglishkids.britishcouncil.org/en/
https://www.lingoda.com/en/english/learning-material/cefr/A1.1
https://aprendafalaringles.com.br/free-online-english-courses/
https://www.repeto.org/learn/english
http://www.speakenglish.biz/
http://www.englishclass101.com/
English writing software
http://www.englishsoftware.org
Languages written with the Latin alphabet
Afrikaans, Alsatian, Bavarian, Cimbrian, Danish, Dutch, Elfdalian, English, Faroese, Flemish, Frisian (East), Frisian (North), Frisian (Saterland), Frisian (West), German, Gothic, Gottscheerish, Gronings, Hunsrik, Icelandic, Limburgish, Low German, Luxembourgish, Mòcheno, Norn, Norwegian, Old English, Old Norse, Pennsylvania German, Ripuarian, Scots, Shetland(ic), Stellingwarfs, Swabian, Swedish, Swiss German, Transylvanian Saxon, Värmlandic, Wymysorys, Yiddish, Yola, Zeelandic
Page last modified: 13.06.23
[top]
You can support this site by Buying Me A Coffee, and if you like what you see on this page, you can use the buttons below to share it with people you know.

If you like this site and find it useful, you can support it by making a donation via PayPal or Patreon, or by contributing in other ways. Omniglot is how I make my living.
Note: all links on this site to Amazon.com, Amazon.co.uk
and Amazon.fr
are affiliate links. This means I earn a commission if you click on any of them and buy something. So by clicking on these links you can help to support this site.
[top]