Karelian is a Finnic language spoken mainly in the Russian Republic of Karelia, and also in Finland. In 2010 there were about 25,600 speakers of Karelian in the Russian Federation, and there were 5,000 in Finland in 2018. Karelian is official considered a dialect of Finnish in Karelia, though there are moves to have it recognised as a second language. East Karelian dialects have little mutual intelligibility with Finnish.
The earliest known example of written Karelian, and of writing in any Finnic language, is a birch bark letter found at Novgorod in 1957 which dates from the early 13th century. It was written in the Cyrillic alphabet and the language is thought to be an archaic form of Olonets Karelian, which is also known as East Karelian or Liwi and is spoken along the Olonka River in the Republic of Karelia.
Until the 19th century, Karelian was rarely written, except by a few individuals, and was not taught in schools. During the 19th century a few books were published in Karelian in the Cyrillic alphabet, including books of prayers, songs, and primers. There was no standard way of writing Karelian at the time, and each writer used a slightly different spelling system.
In 1921, after much debate, Finnish was adopted as the official language of the new Karelian Labour Commune, which became the Karelian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic in 1923. Some publishing in Karelian continued, and the first Karelian newspaper was published in 1929.
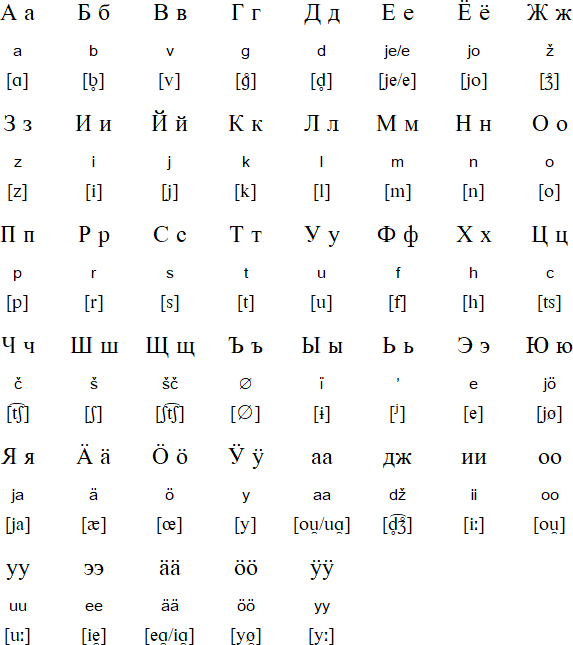
Ф, ц, щ, ъ and ы were only used in names and loanwords.
A version of the Latin alphabet was used for Karelian between 1930-1931 in the Tver Karelian community.
Two ways of writing Karelian with the Cyrillic alphabet were proposed and discussed in 1937, and one of them was adopated in 1938. This became the official standard way to write Karelian in the Karelian SSR and the Tver Region. This was abandoned in 1940 and Finnish became the official language of the Karelian SSR, while most Karelians were expelled from the Tver region and their language was banned.
A new Latin-based alphabet for Karelian known as Olonets Karelian was adopted in 1989. It was named after and used to write one of the dialects of Karelian. This was replaced by the unified Karelian alphabet in 2007, which was slightly modified in 2014 with the addition of the letter C.
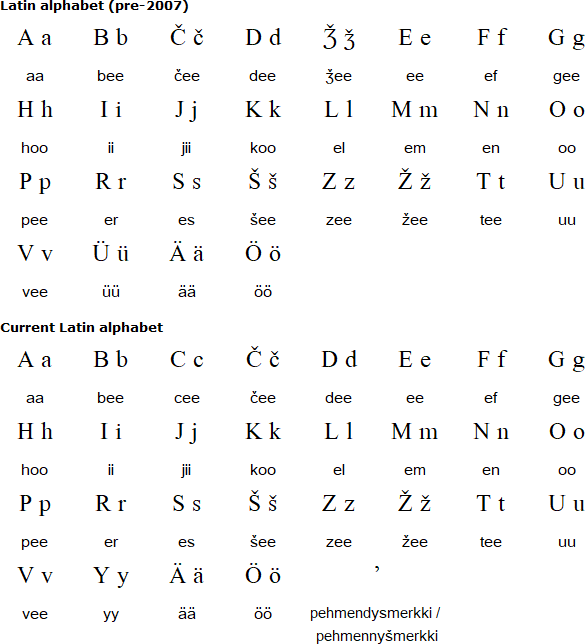
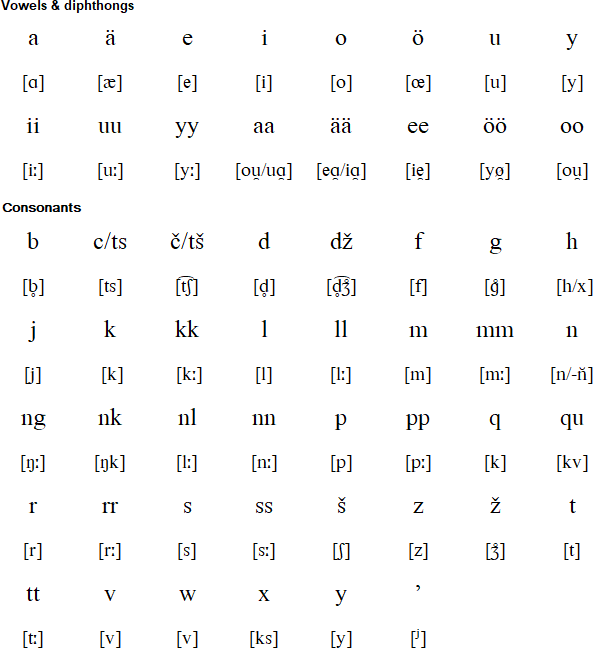
Download an alphabet chart for Karelian (Excel)
Kai rahvas roittahes vällinny da taza-arvozinnu omas arvos da oigevuksis. Jogahizele heis on annettu mieli da omatundo da heil vältämättäh pidäy olla keskenäh, kui vellil.
Каи рахвас роиттахeс вäллиннÿ да таза-арвозинну омас арвос да оигeвуксис. Ёгахизeлe хeис он аннeтту миeли да оматундо да хeил вäлтäмäттäх пидäÿ олла кeскeнäх, куи вeллил.
All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.
(Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights)
This is the earliest known text in Karelian and dates from the beginning of the 13th century.

юмолануолиїнимижи
ноулисѣханолиомобоу
юмоласоудьнииохови
jumolanuoli ï nimizi
nouli se han oli omo bou
jumola soud'ni iohovi
God's arrow, ten [is] your name
This arrow is God's own
The Doom-God leads.
Source: Wikipedia
Details provided by Wolfram Siegel and Michael Peter Füstumum
Information about Karelian | Numbers
Information about Karelian
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karelian_language
https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Карельская_письменность
http://www.eki.ee/books/redbook/karelians.shtml
https://www.ethnologue.com/language/krl
Oldest Karelian text
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Birch_bark_letter_no._292
Online Karelian lessons
http://depvladimir.narod.ru/urokkat/index.html
Online Karelian dictionary (Vepsian-Karelian-Finnish-Voro)
http://www.veps.de/Sanasto/
Online Karelian radio
http://www.karjalankielenseura.fi/radio/
http://www.karjalanradio.narod.ru/audio.html
Estonian, Finnish, Karelian, Kven, Livvi-Karelian, Livonian, Ludic, Meänkieli, Seto, Veps, Võro, Votic
Abaza, Abkhaz, Adyghe, Aghul, Akhvakh, Akkala Sámi, Aleut, Altay, Alyutor, Andi, Archi, Assyrian / Neo-Assyrian, Avar, Azeri, Bagvalal, Balkar, Bashkir, Belarusian, Bezhta, Bosnian, Botlikh, Budukh, Bulgarian, Buryat, Chamalal, Chechen, Chelkan, Chukchi, Chulym, Chuvash, Crimean Tatar, Dargwa, Daur, Dolgan, Dungan, Enets, Erzya, Even, Evenki, Gagauz, Godoberi, Hinukh, Hunzib, Ingush, Interslavic, Itelmen, Juhuri, Kabardian, Kaitag, Kalderash Romani, Kalmyk, Karaim, Karakalpak, Karata, Karelian, Kazakh, Ket, Khakas, Khanty, Khinalug, Khorasani Turkic, Khwarshi, Kildin Sámi, Kili, Komi, Koryak, Krymchak, Kryts, Kubachi, Kumandy, Kumyk, Kurdish, Kyrgyz, Lak, Lezgi, Lingua Franca Nova, Lithuanian, Ludic, Macedonian, Mansi, Mari, Moksha, Moldovan, Mongolian, Montenegrin, Nanai, Negidal, Nenets, Nganasan, Nivkh, Nogai, Old Church Slavonic, Oroch, Orok, Ossetian, Pontic Greek, Romanian, Rushani, Russian, Rusyn, Rutul, Selkup, Serbian, Shor, Shughni, Siberian Tatar, Sirenik, Slovio, Soyot, Tabassaran, Tajik, Talysh, Tat, Tatar, Teleut, Ter Sámi, Tindi, Tofa, Tsakhur, Tsez, Turkmen, Tuvan, Ubykh, Udege, Udi, Udmurt, Ukrainian, Ulch, Urum, Uyghur, Uzbek, Veps, Votic, Wakhi, West Polesian, Xibe, Yaghnobi, Yakut, Yazghulami, Yukaghir (Northern / Tundra), Yukaghir (Southern / Kolyma), Yupik (Central Siberian)
Languages written with the Latin alphabet
Page last modified: 22.02.22
[top]
You can support this site by Buying Me A Coffee, and if you like what you see on this page, you can use the buttons below to share it with people you know.

If you like this site and find it useful, you can support it by making a donation via PayPal or Patreon, or by contributing in other ways. Omniglot is how I make my living.
Note: all links on this site to Amazon.com, Amazon.co.uk
and Amazon.fr
are affiliate links. This means I earn a commission if you click on any of them and buy something. So by clicking on these links you can help to support this site.
[top]